Glossary: Bi-Monthly Pay Schedule

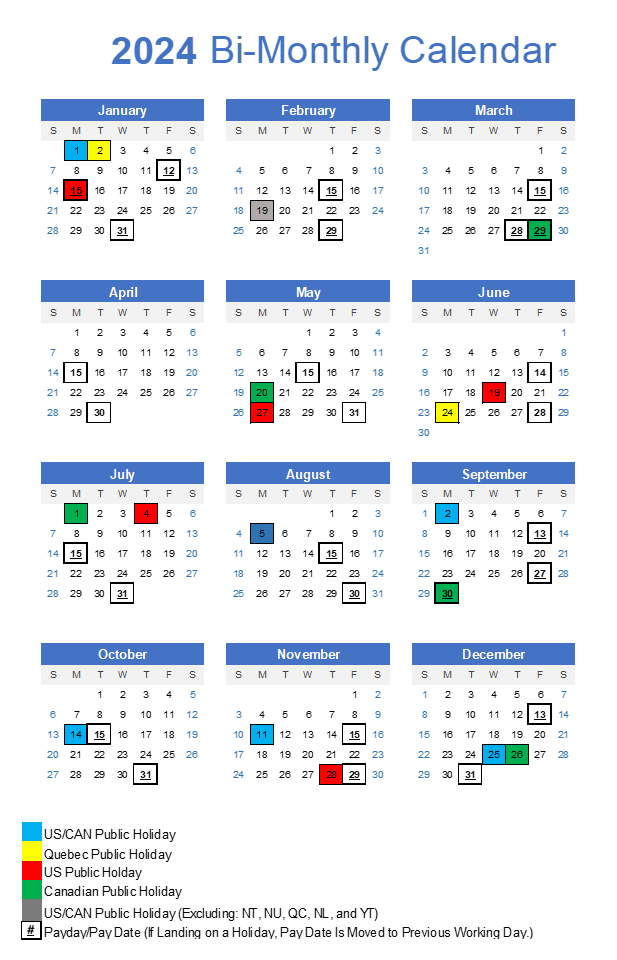
2024 US & Canada Bi-Monthly Payroll Calendar
What is Bi-Monthly Pay?
Bi-monthly pay is a payroll distribution system where employees receive their wages twice each month on specific, pre-arranged dates. Typically, these payments occur on the 1st and the 15th, ensuring that employees know exactly when they will receive their earnings. This schedule results in 24 pay periods throughout the year, offering consistent intervals for budgeting and expense management.
Bi-monthly payment schedules are prevalent across a broad range of sectors, including government, education, and corporate environments. This widespread adoption is due to the balance it provides between frequency and predictability of pay, which suits the budgeting preferences of most employees while maintaining administrative simplicity for payroll departments. Use our Bi-Monthly Gross Pay Calculator to find your wage based on your hourly pay, annual or monthly salary.
Bi-Monthly Vs Semi-Monthly Pay Schedules
While “bi-monthly pay” might sound similar to “semi-monthly pay,” there is a subtle difference:
- Bi-monthly Pay: Payment is issued twice each month, resulting in exactly 24 paychecks each year. The set dates (such as the 1st and 15th) do not vary, regardless of the number of days in the month.
- Semi-Monthly Pay: Though also resulting in 24 pay periods per year, this term is less commonly used and generally encompasses any system where paychecks are issued twice per month without fixed dates.
- Bi-Weekly Pay: This system involves paychecks being issued every two weeks, regardless of the month, which totals 26 paychecks annually. This frequency can lead to varying monthly income totals, which may affect budgeting.
The Importance of Understanding Different Payroll Schedules
For employees, knowing whether you’re on a bi-monthly, semi-monthly, or bi-weekly pay schedule can significantly impact financial management. Each payroll schedule affects how you budget, plan for expenses, and save for future goals. For employers, choosing the right payroll schedule is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency, adhering to budget constraints, and complying with local labor laws. An informed choice about payroll scheduling not only simplifies the administrative workload but also enhances employee satisfaction by providing predictability and security in their financial planning.
How Does Bi-Monthly Payroll Work?
Bi-monthly payroll is structured around two fixed payment dates each month. This method is straightforward: employees receive their wages on two predetermined days, which simplifies both the administrative burden for the payroll department and the financial planning process for employees.
The process starts with the payroll department calculating the total earnings for each employee. This includes their base salary, along with any additional compensations such as overtime, bonuses, or deductions. Once calculations are complete, payments are processed to ensure funds are available in employee bank accounts on the designated payday.
Common Payment Dates
Typically, the most common payment dates in a bi-monthly payroll system are the 1st and the 15th of each month. If these dates fall on a weekend or a public holiday, the payment is usually processed on the last working day before the due date. This adjustment ensures that employees have access to their funds when needed and helps them manage their financial obligations without disruption.

Annual Salary Vs Bi-Monthly Salary
| Annual Salary ($) | Bi-Monthly Salary ($) |
|---|---|
| 30,000 | 1,250 |
| 40,000 | 1,666.67 |
| 50,000 | 2,083.33 |
| 60,000 | 2,500 |
| 70,000 | 2,916.67 |
| 80,000 | 3,333.33 |
| 90,000 | 3,750 |
| 100,000 | 4,166.67 |
| 110,000 | 4,583.33 |
| 120,000 | 5,000 |
| 130,000 | 5,416.67 |
| 140,000 | 5,833.33 |
| 150,000 | 6,250 |

Advantages of Bi-Monthly Payroll
Bi-monthly payroll offers several benefits that can enhance the working relationship between employers and employees. For employers, this payment schedule simplifies the timing of payroll processing and reduces the frequency of payroll runs, thus lowering processing costs and administrative burden. Employees benefit from a predictable payment schedule, which facilitates easier budgeting and financial planning. This consistency in pay dates can also improve job satisfaction and financial security among staff, as they can reliably anticipate when they will receive their income.
Financial Planning: Predictable Payment Schedules Aid in Budgeting
One of the most significant advantages of bi-monthly payroll for employees is the ability to plan their finances with greater certainty. Knowing that paychecks will arrive on specific dates—typically the 1st and 15th of each month—allows individuals to schedule bill payments, savings deposits, and other financial obligations without the worry of timing mismatches that can occur with less regular payroll schedules. This regularity helps avoid late fees on bills and makes it easier to manage cash flow, potentially leading to better credit scores and financial stability.
Administrative Benefits: Simplification of Payroll Processing
From an administrative perspective, bi-monthly payroll is easier to manage than more frequent payroll cycles. Processing payroll only twice a month reduces the opportunities for errors during data entry and allows for a more thorough review of payroll adjustments, such as overtime, bonuses, and deductions, before they are finalized. This schedule also aligns well with monthly accounting periods, making financial reporting and tax preparation more straightforward. Moreover, by having fixed dates each month for payroll, HR and payroll departments can streamline their workflows, focus more on strategic tasks, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements more consistently.
Efficiency in Resource Allocation
Employers also find that a bi-monthly payroll system allows for better allocation of human resources. Payroll staff can predict workload peaks and allocate time and resources more effectively, avoiding the stress and overtime often associated with more frequent payroll periods. This improved efficiency can reduce operational costs and contribute to a more focused and productive administrative team.
How to Calculate Bi-Monthly Salary
Calculating a bi-monthly salary from an annual salary is a straightforward process that involves simple arithmetic. This calculation helps employees understand how much they will receive in each paycheck before taxes and other deductions. Here’s how to do it:
Step-by-Step Guide
Identify the Annual Salary: Start with the total annual gross salary. This is the amount the employee earns in a year before any deductions.
Divide by the Number of Pay Periods: Since bi-monthly pay involves 24 paychecks per year (two per month), divide the annual salary by 24.
Bi-Monthly Salary = Annual Salary/24Adjust for Taxes and Deductions: To find the net bi-monthly pay, subtract any federal, state, and local taxes, along with other deductions like health insurance and retirement contributions from the gross bi-monthly amount calculated in step 2.
Examples with Different Annual Salaries
Example 1: Annual Salary of $60,000
- Gross Bi-Monthly Salary Calculation:60,000/24 = 2,500
- Assuming standard deductions and taxes (approx. 30%), the net bi-monthly salary might be around:
- 2,500−(0.30×2,500)=1,750
Example 2: Annual Salary of $75,000
- Gross Bi-Monthly Salary Calculation:
- 75,000/24 = 3,125
- With similar deductions as in Example 1, the net bi-monthly salary could be:
- 3,125−(0.30×3,125) = 2,187.50
Example 3: Annual Salary of $100,000
- Gross Bi-Monthly Salary Calculation:
- 100,000/24 = 4,166.67
- Again, subtracting estimated taxes and deductions:
- 4,166.67−(0.30×4,166.67) = 2,916.67

Common Questions About Bi-Monthly Payroll
Understanding bi-monthly payroll involves getting to grips with how pay periods work, the handling of specific timing issues like weekends and holidays, and the implications for tax withholdings. Here are answers to some of the most common questions:
How many bi-monthly pay periods are there in a year?
A bi-monthly payroll schedule means that employees receive their wages twice each month, typically on predetermined dates such as the 1st and the 15th. This setup results in a total of 24 pay periods per year. It is crucial for employees and employers to understand this schedule for financial planning and reporting purposes.
What happens if payment dates fall on weekends or holidays?
When scheduled payment dates fall on a weekend or a public holiday, the pay date is usually adjusted to the nearest working day before the weekend or holiday. This adjustment ensures that employees have access to their funds when needed, which is particularly important for managing bill payments and other financial commitments. Employers need to communicate these adjustments clearly and consistently to avoid confusion and ensure smooth financial operations.
Differences in tax withholdings for bi-monthly versus bi-weekly paychecks
Tax withholdings can differ between bi-monthly and bi-weekly payment schedules due to the number of paychecks employees receive per year:
- Bi-monthly Paychecks: Employees receive 24 paychecks per year, and the amount of tax withheld per paycheck is calculated based on this frequency. The consistency in payment amounts can make it easier for employees to estimate their yearly tax liabilities.
- Bi-weekly Paychecks: In contrast, bi-weekly schedules involve 26 paychecks per year. Although the individual paycheck amounts might be smaller compared to bi-monthly paychecks, the total amount of tax withheld over the year might slightly differ because of the additional pay periods. Employees might see minor differences in how much tax is taken from each paycheck, potentially affecting their total tax liability at the end of the year.
Bi-Monthly vs. Semi-Monthly vs. Bi-Weekly Payroll
Understanding the nuances between different payroll schedules is crucial for both employees and employers, as the choice impacts financial planning and payroll management. Here’s a breakdown of the three common types of payroll schedules: bi-monthly, semi-monthly, and bi-weekly.
Bi-Monthly Payroll
- Description: Employees are paid twice a month on predetermined fixed dates, typically the 1st and 15th. This results in exactly 24 paychecks per year.
- Paycheck Amount: Paycheck amounts are generally higher because the salary is divided into fewer installments (24 versus 26 for bi-weekly).
- Frequency: Pay is received consistently twice each month, which simplifies budgeting.
- Pros: Predictable pay dates facilitate easier budget management and financial planning. Lower frequency of payroll processing reduces administrative costs.
- Cons: Adjusting to less frequent paychecks requires careful financial planning to cover all expenses throughout the month.
Semi-Monthly Payroll
- Description: Similar to bi-monthly, with employees also receiving 24 paychecks per year. However, the pay dates aren’t fixed (e.g., might be the last workday before the 15th and the last day of the month).
- Paycheck Amount: Similar to bi-monthly payroll, with each paycheck representing approximately 1/24th of the annual salary.
- Frequency: Paychecks are issued semi-monthly but without the fixed schedule of bi-monthly, which can vary slightly based on the calendar.
- Pros: Still provides a consistent number of paychecks which helps with budgeting.
- Cons: Slightly less predictable than bi-monthly due to varying pay days, which can complicate budgeting slightly.
Bi-Weekly Payroll
- Description: Employees are paid every two weeks, usually on a specific day of the week, resulting in 26 pay periods per year.
- Paycheck Amount: Each paycheck is slightly smaller because the annual salary is divided by 26 rather than 24.
- Frequency: Paychecks are more frequent, which can help spread out monthly budgeting more evenly.
- Pros: Frequent paychecks may help with cash flow for employees who find it challenging to budget over longer periods.
- Cons: The two extra paychecks per year can complicate budgeting, especially as two months will have three pay periods. Also, slightly more complex for payroll processing.
Choosing the Best Option
The best payroll schedule depends on the specific needs of both the organization and its employees:
- For Stable Budgeting: Bi-monthly and semi-monthly are preferred for their predictability and easier financial management.
- For Better Cash Flow: Bi-weekly might be beneficial for those who prefer more frequent payments to manage ongoing expenses.
- Administrative Perspective: Bi-monthly might be easier and less costly to administer due to fewer payroll runs.

Legal Considerations and Compliance
Navigating the legal landscape of payroll compliance is crucial for any organization. Understanding and adhering to the legal requirements of bi-monthly payroll schedules can help avoid costly penalties and ensure a harmonious workplace. Here’s a comprehensive overview of what employers need to know.
Overview of Legal Requirements
- Federal and State Regulations: While federal laws set the groundwork for minimum wage, overtime pay, and record-keeping requirements, state laws can vary significantly in terms of payday regulations. For example, some states mandate that employees be paid at least twice a month, while others have more flexible guidelines.
- State-Specific Payday Requirements: Many states have specific payday requirements that must be followed. For instance, California requires that employees be paid at least twice a month on specific days, as outlined by the employer in their payroll policies.
- Direct Deposit Laws: Employers offering direct deposit must comply with state laws that regulate this method. Some states allow employers to require direct deposit only if certain conditions are met, such as obtaining the employee’s consent.
- Final Paycheck Laws: Nearly every state has regulations about when a terminated employee must receive their final paycheck, and these rules can affect how bi-monthly pay schedules are managed during termination procedures.
Tips for Employers on Compliance with Labor Laws
- Understand Local Laws: It’s essential for employers to understand not only the federal laws but also the state and local laws that affect payroll. This means keeping up to date with changes to ensure compliance at all times.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular payroll audits can help catch and correct compliance issues before they become problematic. This includes reviewing that all employees are paid on time according to the established bi-monthly schedule and ensuring that record-keeping practices meet legal standards.
- Clear Payroll Policies: Employers should clearly outline their payroll policies, including the bi-monthly pay schedule, in employee handbooks. This transparency helps prevent misunderstandings and provides a reference that can be useful during disputes.
- Employee Training and Communication: Regular training sessions for both payroll staff and other employees can help ensure that everyone understands their rights and responsibilities under the payroll policies in place.
Links to Government Resources for Further Reading
- U.S. Department of Labor – Wage and Hour Division: This site provides resources on federal wage laws, including those relating to minimum wages and overtime.
- National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) Payday Requirements: Offers a comprehensive overview of payday requirements by state, helping employers and employees understand specific local regulations.
- IRS – Employer’s Tax Guide: Details federal tax withholding and reporting requirements, crucial for proper payroll processing.
Disclaimer: The content provided on this webpage is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information presented here, the details may change over time or vary in different jurisdictions. Therefore, we do not guarantee the completeness, reliability, or absolute accuracy of this information. The information on this page should not be used as a basis for making legal, financial, or any other key decisions. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified professional or expert in the relevant field for specific advice, guidance, or services. By using this webpage, you acknowledge that the information is offered “as is” and that we are not liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content, nor for any actions taken based on the information provided. We shall not be held liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, consequential, or punitive damages arising out of your access to, use of, or reliance on any content on this page.
Trusted By
Trusted by 3.2M+ Employees: 21 Years of Service Across Startups to Fortune 500 Enterprises
Join our ever-growing community of satisfied customers today and experience the unparalleled benefits of TimeTrex.









Strength In Numbers
Join The Companies Already Benefiting From TimeTrex
Time To Clock-In
Start your 30-day free trial!
Experience the Ultimate Workforce Solution and Revolutionize Your Business Today
- Eliminate Errors
- Simple & Easy To Use
- Real-time Reporting

Saving businesses time and money through better workforce management since 2003.
Copyright © 2026 TimeTrex. All Rights Reserved.


